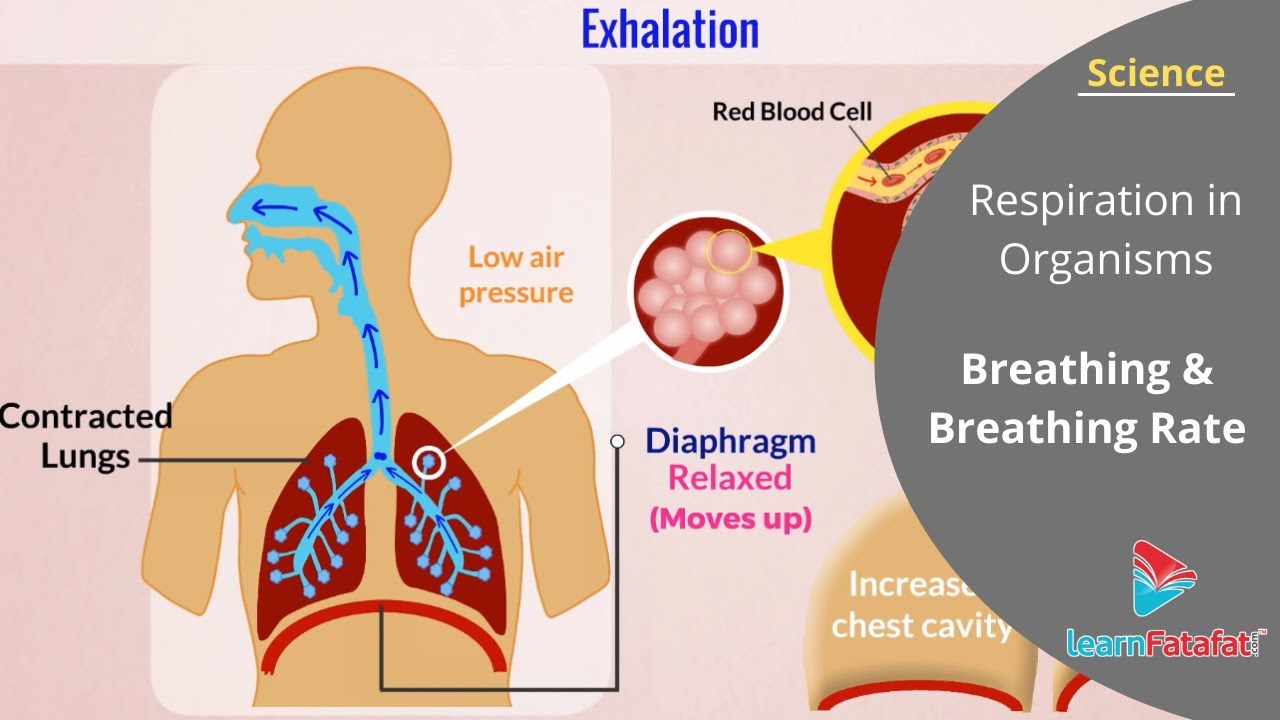
What is breathing rate?
Breathing rate, also known as respiratory rate, refers to the number of breaths a person takes per minute. It is a vital sign that provides valuable insights into a person's overall health and well-being. Normal breathing rates vary depending on age, with newborns typically having higher rates than adults. For instance, a healthy adult at rest usually has a breathing rate between 12 and 16 breaths per minute.
Measuring breathing rate is a common practice in medical settings, as it can help healthcare professionals assess a person's respiratory function and detect any potential respiratory issues. Monitoring breathing rate is particularly important for critically ill patients, such as those with respiratory conditions or who have undergone surgery.
Understanding breathing rate is essential for maintaining overall health. It can serve as an early indicator of respiratory distress or other medical conditions that may require prompt medical attention. Therefore, it is important to be aware of your breathing rate and consult a healthcare professional if you experience any significant changes or difficulties breathing.
Breathing Rate Definition
Breathing rate, also known as respiratory rate, is a crucial indicator of overall health and well-being. Here are ten key aspects that delve into its definition and significance:
- Measurement: Counting the number of breaths per minute.
- Normal Range: Varies with age, typically 12-16 breaths per minute for adults at rest.
- Assessment Tool: Used by healthcare professionals to evaluate respiratory function.
- Vital Sign: Provides insights into overall health and can indicate potential health issues.
- Respiratory Conditions: Higher or lower than normal rates may suggest respiratory distress or other conditions.
- Monitoring: Important for critically ill patients to assess respiratory function.
- Newborns: Typically have higher breathing rates than adults.
- Sleep: Breathing rates can vary during different sleep stages.
- Exercise: Physical activity can increase breathing rate.
- Emotions: Anxiety or stress can affect breathing rate.
These aspects highlight the importance of understanding breathing rate as a vital sign. Monitoring breathing rates can provide early detection of respiratory issues and contribute to overall health management. It is essential to be aware of your breathing rate and seek medical attention if you experience any significant changes or difficulties breathing.
Measurement
Counting the number of breaths per minute is a fundamental aspect of breathing rate definition. It provides a quantitative measure of respiratory function, allowing healthcare professionals to assess an individual's overall health and detect any potential respiratory issues. By manually counting the number of breaths taken over a specific time frame, usually one minute, clinicians can determine the breathing rate.
This measurement holds significant importance as it serves as a vital sign, reflecting the body's metabolic activity and overall physiological state. Normal breathing rates vary depending on age, with adults typically having a resting rate between 12 and 16 breaths per minute. Deviations from these normal ranges may indicate underlying health conditions, such as respiratory distress, metabolic disturbances, or neurological impairments.
Monitoring breathing rate is crucial in various clinical settings, including emergency departments, intensive care units, and during surgical procedures. It helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care, including the need for respiratory support or further diagnostic testing. By understanding the connection between measuring breaths per minute and breathing rate definition, clinicians can effectively evaluate respiratory function and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Normal Range
The normal range of breathing rates varies depending on age, with adults typically having a resting rate between 12 and 16 breaths per minute. This facet of breathing rate definition highlights the dynamic nature of respiratory function and its relationship to different stages of life.
- Age-Related Variations: Breathing rates tend to be higher in newborns and infants, gradually decreasing with age. This variation is attributed to differences in metabolic rates and lung development.
- Physiological Adaptations: The resting breathing rate can also be influenced by physiological adaptations, such as altitude and pregnancy. Higher altitudes, for instance, may lead to slightly elevated breathing rates due to reduced oxygen availability.
- Individual Differences: Within the normal range, individuals may have slightly different breathing rates based on factors such as fitness level, body size, and overall health status.
- Clinical Significance: Understanding the normal breathing rate range is crucial for healthcare professionals as deviations from these values may indicate underlying respiratory conditions or other health issues.
In summary, the facet "Normal Range: Varies with age, typically 12-16 breaths per minute for adults at rest" emphasizes the variability of breathing rates across different age groups and highlights the importance of considering age-specific norms when assessing respiratory function. It also underscores the influence of physiological factors and individual differences on breathing patterns, reinforcing the multifaceted nature of breathing rate definition.
Assessment Tool
The connection between "Assessment Tool: Used by healthcare professionals to evaluate respiratory function" and "breathing rate definition" lies in the crucial role that breathing rate plays as a vital sign for assessing respiratory function. Breathing rate is a quantitative measure that reflects the rate at which an individual breathes, and it is a key parameter used by healthcare professionals to evaluate the overall respiratory health of a patient.
As part of a comprehensive respiratory assessment, measuring breathing rate provides valuable insights into the patient's respiratory status. This information can help identify potential respiratory issues, such as respiratory distress or abnormalities in the respiratory rhythm. By monitoring breathing rate over time, healthcare professionals can track changes in respiratory function and assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
Examples of real-life applications of breathing rate assessment include:
- In emergency departments, rapid breathing rates may indicate respiratory distress and require immediate medical attention.
- In intensive care units, close monitoring of breathing rates is essential for managing critically ill patients who may require mechanical ventilation.
- During surgical procedures, breathing rate is monitored to ensure adequate ventilation and oxygenation.
Understanding the importance of breathing rate as an assessment tool is crucial for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care. By incorporating breathing rate measurement into their assessments, they can effectively evaluate respiratory function, detect respiratory issues early on, and provide appropriate treatment.
Vital Sign
The facet "Vital Sign: Provides insights into overall health and can indicate potential health issues" underscores the significance of breathing rate as a vital physiological parameter that reflects the overall health and well-being of an individual. By measuring breathing rate, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into a patient's respiratory function and assess their overall health status.
- Facet 1: Respiratory Function Assessment
Breathing rate serves as a key indicator of respiratory function. It can help identify respiratory distress, such as shortness of breath or labored breathing, which may indicate underlying respiratory conditions like asthma, pneumonia, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Facet 2: Metabolic Rate and Acid-Base Balance
Breathing rate is closely linked to metabolic rate and acid-base balance. Alterations in breathing rate can affect the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood, which can have implications for overall health. For instance, rapid breathing (hyperventilation) can lead to respiratory alkalosis, while slow breathing (hypoventilation) can cause respiratory acidosis.
- Facet 3: Neurological Function
Breathing rate can also provide insights into neurological function, as the respiratory center in the brainstem controls breathing patterns. Changes in breathing rate, such as Cheyne-Stokes respiration or ataxic breathing, may indicate neurological disorders or injuries.
- Facet 4: Monitoring Treatment Response
Measuring breathing rate is crucial in monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for respiratory conditions. For example, in patients with asthma, tracking breathing rate can help assess the response to bronchodilator therapy.
In summary, the vital sign aspect of breathing rate definition highlights its critical role in evaluating respiratory function, metabolic balance, neurological function, and monitoring treatment response. By understanding these facets, healthcare professionals can effectively assess overall health and identify potential health issues, leading to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Respiratory Conditions
The link between "Respiratory Conditions: Higher or lower than normal rates may suggest respiratory distress or other conditions" and "breathing rate definition" lies in the crucial role that breathing rate plays as an indicator of respiratory health. Deviations from normal breathing rates can signal underlying respiratory issues or other health conditions, making it an essential factor in clinical assessments.
- Facet 1: Respiratory Distress
Elevated breathing rates (tachypnea) can be a sign of respiratory distress, a condition in which the body struggles to meet its oxygen demands. This can occur in various scenarios, such as asthma attacks, pneumonia, or pulmonary embolism.
- Facet 2: Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis
Abnormally slow breathing rates (bradypnea) can lead to respiratory acidosis, a condition characterized by an increase in blood carbon dioxide levels. Conversely, rapid breathing rates can result in respiratory alkalosis, where blood carbon dioxide levels decrease.
- Facet 3: Neurological Disorders
Breathing rate abnormalities can also indicate neurological disorders that affect the respiratory center in the brainstem. For instance, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, characterized by alternating periods of rapid and shallow breathing, is associated with certain neurological conditions.
- Facet 4: Metabolic Disorders
Changes in breathing rate can be a compensatory response to metabolic disorders. For example, diabetic ketoacidosis, a metabolic condition, can lead to rapid breathing (Kussmaul respiration) to eliminate excess ketones.
In summary, the facet "Respiratory Conditions: Higher or lower than normal rates may suggest respiratory distress or other conditions" emphasizes the significance of breathing rate as a vital sign in identifying respiratory issues and other health conditions. Understanding the implications of abnormal breathing rates is crucial for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about patient care and provide timely interventions.
Monitoring
The connection between "Monitoring: Important for critically ill patients to assess respiratory function" and "breathing rate definition" lies in the crucial role of breathing rate as a vital sign for evaluating respiratory health, especially in critically ill patients. Monitoring breathing rate provides valuable insights into the patient's respiratory status, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment and care.
Critically ill patients, such as those with severe respiratory conditions, often require close monitoring of their breathing rates. This is because changes in breathing rate can be an early indicator of respiratory distress or deterioration. By continuously monitoring breathing rates, healthcare professionals can promptly identify any abnormalities and intervene appropriately, potentially improving patient outcomes.
For instance, in intensive care units (ICUs), breathing rate is one of the key vital signs monitored along with heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. Continuous monitoring of breathing rate allows healthcare professionals to detect subtle changes that may indicate respiratory issues, such as ventilator-associated pneumonia or sepsis. Early detection and intervention can significantly impact patient recovery and reduce the risk of complications.
In summary, the facet "Monitoring: Important for critically ill patients to assess respiratory function" highlights the practical significance of breathing rate monitoring in clinical settings, particularly for critically ill patients. Understanding the connection between breathing rate definition and monitoring is essential for healthcare professionals to provide optimal care and improve patient outcomes.
Newborns
The facet "Newborns: Typically have higher breathing rates than adults" is closely linked to "breathing rate definition" because it highlights an essential characteristic of breathing patterns in newborns. Understanding this facet enhances our comprehension of normal breathing rates and their variations across different age groups.
- Facet 1: Metabolic Rate and Oxygen Demand
Newborns have higher metabolic rates compared to adults, meaning their bodies require more oxygen to support their rapid growth and development. This increased oxygen demand translates into a higher respiratory rate to meet the metabolic needs.
- Facet 2: Lung Development
The lungs of newborns are still developing, and their airways are narrower than those of adults. This can lead to increased airway resistance, requiring a faster breathing rate to maintain adequate ventilation.
- Facet 3: Neurological Factors
The respiratory center in the brainstem, which controls breathing patterns, is less mature in newborns. This immaturity can contribute to variations in breathing rates and may lead to temporary episodes of apnea (cessation of breathing).
- Facet 4: Thermoregulation
Newborns have a larger surface area-to-volume ratio compared to adults, making them more susceptible to heat loss. In response, they may increase their breathing rates to generate more heat through metabolic processes.
In summary, the facet "Newborns: Typically have higher breathing rates than adults" provides insights into the unique respiratory characteristics of newborns. Understanding these facets is crucial for healthcare professionals to assess respiratory function in newborns accurately and provide appropriate care.
Sleep
The connection between "Sleep: Breathing rates can vary during different sleep stages" and "breathing rate definition" lies in the intricate relationship between breathing patterns and sleep cycles. Breathing rate is a vital sign that provides insights into respiratory function, and understanding its variations during sleep is crucial for assessing overall health and well-being.
- Facet 1: REM Sleep
During rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, characterized by vivid dreams, breathing rates tend to be faster and more irregular. This is due to increased metabolic activity in the brain during this sleep stage.
- Facet 2: Non-REM Sleep
Non-REM sleep consists of three stages, each with distinct breathing patterns. In stage 1, breathing rates are generally slower and more regular than during wakefulness. In stages 2 and 3, breathing rates further decrease and become more stable.
- Facet 3: Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses can lead to significant reductions in blood oxygen levels and can disrupt normal sleep patterns. Sleep apnea can be caused by various factors, including airway obstruction or abnormal breathing control mechanisms.
- Facet 4: Sleep-Disordered Breathing
Sleep-disordered breathing encompasses a range of conditions that affect breathing during sleep, including snoring, upper airway resistance syndrome, and central sleep apnea. These conditions can lead to fragmented sleep and daytime sleepiness.
In summary, the facet "Sleep: Breathing rates can vary during different sleep stages" highlights the dynamic nature of breathing rates across different sleep cycles. Understanding these variations is essential for healthcare professionals to evaluate sleep quality, identify potential sleep disorders, and provide appropriate treatment.
Exercise
The connection between "Exercise: Physical activity can increase breathing rate." and "breathing rate definition" lies in the physiological response to physical exertion. Breathing rate is a vital sign that reflects the body's oxygen demand and carbon dioxide production. During exercise, the body's metabolic rate increases, leading to a corresponding increase in oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production. To meet this increased demand, the respiratory system responds by increasing breathing rate and depth.
Understanding the link between exercise and increased breathing rate is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights the dynamic nature of breathing rate, which is not solely determined by resting conditions but also by physiological demands. Secondly, it emphasizes the importance of considering physical activity levels when assessing breathing rate in clinical settings. For instance, a higher breathing rate in an athlete during a workout may be a normal physiological response rather than an indication of respiratory distress.
In summary, the facet "Exercise: Physical activity can increase breathing rate." provides insights into the physiological adaptations that occur during exercise, showcasing the close relationship between breathing rate and the body's metabolic demands. Comprehending this connection is essential for healthcare professionals to accurately interpret breathing rate measurements and assess respiratory function in various contexts.
Emotions
The connection between "Emotions: Anxiety or stress can affect breathing rate" and "breathing rate definition" lies in the profound influence that emotions and psychological factors can have on respiratory function. Breathing rate, a vital sign that reflects the body's oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, can be significantly altered by emotional states such as anxiety or stress.
- Facet 1: Autonomic Nervous System Response
Anxiety and stress trigger the activation of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary bodily functions, including breathing. This activation can lead to increased sympathetic activity, resulting in faster and shallower breathing patterns.
- Facet 2: Hyperventilation
In severe anxiety or panic attacks, hyperventilation can occur. This is characterized by rapid and deep breathing, which can lead to an imbalance in blood pH levels, causing symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and tingling sensations.
- Facet 3: Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, such as fear, anxiety, and depression, can also influence breathing patterns. These emotions can lead to altered breathing patterns, including breath-holding, sighing, or shallow breathing.
- Facet 4: Implications for Breathing Rate Definition
Understanding the impact of emotions on breathing rate is crucial for healthcare professionals to accurately interpret breathing rate measurements and assess respiratory function. It highlights the need to consider psychological factors when evaluating breathing patterns, especially in cases where no apparent physical cause is identified.
In summary, the facet "Emotions: Anxiety or stress can affect breathing rate" provides insights into the complex interplay between emotional states and respiratory function. Comprehending this connection is essential for healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive patient care and address the potential impact of psychological factors on breathing patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions on Breathing Rate
Here are some commonly asked questions and their answers to provide a comprehensive understanding of breathing rate definition and its significance:
Question 1: What is a normal breathing rate?A normal breathing rate for adults at rest typically ranges between 12 to 16 breaths per minute. However, it is important to note that breathing rates can vary based on factors such as age, level of physical activity, and overall health.
Question 2: How is breathing rate measured?Breathing rate is usually measured by counting the number of breaths a person takes per minute. This can be done manually by observing the rise and fall of the chest or using a stethoscope to listen to the breath sounds. Some medical devices can also measure breathing rate continuously.
Question 3: Why is breathing rate important?Breathing rate is a vital sign that provides valuable insights into a person's overall health and well-being. It can indicate potential respiratory issues, metabolic disturbances, or neurological impairments.
Question 4: What causes abnormal breathing rates?Abnormal breathing rates, such as rapid breathing (tachypnea) or slow breathing (bradypnea), can be caused by various factors, including respiratory conditions, metabolic disorders, neurological disorders, and certain medications.
Question 5: How is abnormal breathing rate treated?Treatment for abnormal breathing rates depends on the underlying cause. It may involve medications, oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, or addressing the underlying medical condition.
Question 6: When should I seek medical attention for abnormal breathing rate?If you experience persistent changes in your breathing rate, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or confusion, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Summary: Breathing rate is a crucial vital sign that reflects respiratory function and overall health. Understanding normal breathing rates and the factors that can affect them is essential for early detection and management of potential health issues.
Transition to the Next Section: For further exploration of breathing rate definition, let's delve into its importance in various clinical settings.
Conclusion
In summary, breathing rate definition encompasses the measurement and interpretation of the number of breaths a person takes per minute. It serves as a vital sign, providing valuable insights into respiratory function, overall health, and well-being. Understanding breathing rate is crucial for healthcare professionals to assess respiratory status, detect potential health issues, and monitor treatment effectiveness.
The exploration of breathing rate definition in this article highlights its significance in various clinical settings. Recognizing normal breathing rates and the factors that influence them empowers individuals to monitor their own breathing patterns and seek medical attention when necessary. By promoting a comprehensive understanding of breathing rate definition, this article aims to contribute to improved respiratory health outcomes and overall well-being.
Article Recommendations
- Germania Insurance Amphitheater
- Rodney Alcala On Dating Game Video
- East Multnomah Soil And Water Conservation District